Four Types of Macromolecules
Find all the answers for your macromolecule worksheets and exams in the video and info below.
Thanks for stopping by today we're gonna talk about macromolecules.
Macromolecules are large structures that make up all living organisms. All macromolecules have small sub-units called monomers which bind together to form larger units called polymers. There are four classes of macromolecules:
Carbohydrate structure and function
Carbohydrates are the main fuel source for most living organisms as well as a structural component for many plants. The monomers for carbohydrates are called monosaccharides, saccharide means sugar so monosaccharides one sugar. These are simple sugars like glucose, fructose, and ribose.
Common monosaccharides include glucose and fructose. Image adapted from OpenStax Biology.
The polymers are called polysaccharides, and they are long chains of monomers or monosaccharides. Common polysaccharides include carbohydrates for energy storage like starch in plants and glycogen in animals. Structural carbohydrates include cellulose and plants and chitin in insects.
Watch this video about carbohydrates to learn more.
Lipid structure and function
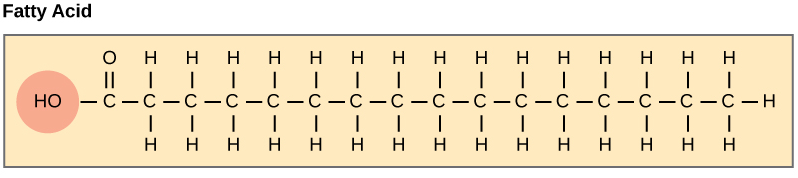
Moving on to lipids. Lipids have a variety of functions in living organisms and there are a lot of compounds lumped into the category of lipids. One characteristic that makes all lipids similar is that they are hydrophobic, so they repel water. Some major lipid functions include energy storage (as fats), cell membrane formation, and steroid function. They have no real monomers, they just are what they are.
Fatty acids are the base structure for many lipids. Image adapted from OpenStax Biology.
Fats (or fatty acids) include triglycerides as well as saturated unsaturated fats. You also have phospholipids, which form the cellular membranes. Then steroids, which include all sex hormones. All the steroids form from a cholesterol base. All of those are included in the macromolecule category of lipids, so it's pretty diverse.
Watch this video about lipids to learn more.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, there are 20 different amino acids. Image adapted from OpenStax Biology.
Protein structure and function
Proteins are involved in nearly all cellular functions and are a major part of all living organisms. Their monomers are called amino acids and there are 20 different amino acids.
Their polymers are called polypeptides. Polypeptides are formed by binding amino acids together in the translation phase of protein synthesis. These polypeptide chains are then folded into certain structures and the structure determine the function. Enzymes are a major category of proteins that do a lot of work in the cells, they are pretty awesome!
Watch this video about proteins to learn more.
Nucleic Acid structure and function
Thymine, adenine, guanine, and cytosine are the nucleotides that make up the nucleic acid, DNA. Image adapted from OpenStax Biology.
Nucleic acids store, transmit, and express genetic information. Their monomers are called nucleotides like adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine, and uracil.
You may be familiar with these terms from studying DNA and RNA. And that's what their polymers are, they're called polynucleotides and they're strands of DNA and RNA.
Watch this video about nucleic acids to learn more.